本节主要内容:
1.实例化Spring容器示例
2.利用Spring容器创建JavaBean对象 3.如何控制Bean实例化 4.利用Spring实现bean属性setter方式注入 5.利用构造器参数实现依赖属性的注入 6.利用Spring的自动装配功能实现自动属性注入
本文作者:souvc
本文出处:
1 实例化Spring容器示例
1.1 问题
使用ApplicationContext的方式实例化Spring容器。
1.2 方案
使用ApplicationContext的方式实例化Spring容器的核心代码如下:
String conf = "applicationContext.xml"; ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(conf);
1.3 步骤
步骤一:新建工程,导入jar包
新建名为 SouvcSpringIOC 的web工程,在该工程导入5个Spring相关jar包。
commons-logging.jar spring-core.jar spring-context.jar spring-beans.jar spring-expression.jar
网盘下载jar包 :http://yunpan.cn/cQJhPMPRZeLH7 访问密码 2bf8
步骤二:新建Spring配置文件
与src目录下新建Spring配置文件 applicationContext.xml 。该文件名为Spring默认的配置文件名,也可以自由定义名称。
步骤三:新建类TestCase
导入JUnit4 , 用于软件的单元测试.
新建类TestCase,在类中使用ApplicationContext的方式实例化Spring容器。
在TestCase类中添加测试方法testInitContext():
/** 测试实例化Spring容器示例 */ @Test public void testInitContext() { String conf = "applicationContext.xml"; ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(conf); System.out.println(ac); }
步骤四:运行testInitContext()方法
运行testInitContext()方法,控制台输出结果
org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext@5a77a7f9: startup date [Tue Jun 16 17:22:35 CST 2015]; root of context hierarchy
控制台输出以上的信息,说明实例化Spring容器成功。
1.4 完整代码
TestCase类的完整代码如下:
package com.souvc.test;import org.junit.Test;import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;public class TestCase { /** 测试实例化Spring容器示例 */ @Test public void testInitContext() { String conf = "applicationContext.xml"; ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(conf); System.out.println(ac); }}
applicationContext.xml完整代码如下:
2 利用Spring容器创建JavaBean对象
2.1 问题
测试Spring支持的多种JavaBean对象创建方式:
1. 用构造器来实例化的方式。
利用Spring调用构造器 GregorianCalendar 创建 Calendar实例.
2. 使用静态工厂方法实例化的方式。
利用Spring调用 Calendar 的静态工厂方法getInstance() 创建 Calendar实例.
3. 使用实例工厂方法实例化的方式。
利用Spring创建 GregorianCalendar 对象作为工厂, 调用getTime()方法创建Date类型对象实例.
2.2 方案
1. 用构造器来实例化的方式的配置代码如下:
bean标记中id属性calendarObj1用于定义bean名字, 是程序代码中获得Spring管理bean对象的标识, 这个名字不能重复, class用于指定创建对象的类GregorianCalendar, Spring会自动的调用GregorianCalendar类的默认构造器创建bean对象实例.
2. 使用静态工厂方法实例化的方式的配置代码如下:
bean标记中id属性calendarObj2用于定义bean名字, 是程序代码中获得Spring管理bean对象的标识, 这个名字不能重复, class属性用于指定创建对象的工厂类Calendar, factory-method属性用于指定创建对象的静态工厂方法getInstance, Spring会自动的调用工厂类Calendar静态工厂方法getInstance创建bean对象实例.
3. 使用实例工厂方法实例化的方式的配置代码如下:
这里定义了两个bean, 其中一个bean calendarObj3是用于创建 dateObj 对象的实例工厂.
另外一个bean标记中id属性dateObj用于定义bean名字, 是程序代码中获得Spring管理bean对象的标识, 这个名字不能重复, factory-bean属性用于指定创建对象的工厂对象calendarObj3, 前面定义的一个bean, factory-method属性用于指定创建对象的工厂方法getTime, Spring会自动的调用工厂类Calendar静态工厂方法getInstance创建bean对象实例.
2.3 步骤
步骤一:配置 applicationContext.xml, 增加Bean对象创建声明
代码如下所示:
步骤二:在TestCase类中增加测试方法testCreateBeanObject,测试Spring创建对象的结果
先创建Spring容器对象, 再调用getBean方法获得Spring创建的对象实例,并且利用输出语句测试对象是否存在. 这个代码中要注意: getBean方法的参数必须是上一个步骤中定义的bean标记上的id属性的值, 否则会出现运行异常.
代码如下所示:
/** 测试Spring支持的多种JavaBean对象创建方式 */ @Test public void testCreateBeanObject() { // 实例化Spring容器示例 String conf = "applicationContext.xml"; ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(conf); // 1. 用构造器来实例化的方式。 // 利用Spring调用构造器 GregorianCalendar 创建 Calendar实例. // Calendar cal1 = (Calendar)ac.getBean("calendarObj1"); //方式1 Calendar cal1 = ac.getBean("calendarObj1", Calendar.class); // 方式2 System.out.println("cal1:" + cal1); // 2. 使用静态工厂方法实例化的方式。 // 利用Spring调用 Calendar 的静态工厂方法getInstance() 创建 Calendar实例. Calendar cal2 = ac.getBean("calendarObj2", Calendar.class); System.out.println("cal2:" + cal2); // 3. 使用实例工厂方法实例化的方式。 // 利用Spring创建 GregorianCalendar 对象作为工厂, 调用getTime()方法创建Date类型对象实例. Date date = ac.getBean("dateObj", Date.class); System.out.println("date:" + date); }
步骤三:运行测试方法测试bean实例化
控制台输出结果如下所示:
cal1:java.util.GregorianCalendar[time=1434446926808,areFieldsSet=true,areAllFieldsSet=true,lenient=true,zone=sun.util.calendar.ZoneInfo[id="Asia/Shanghai",offset=28800000,dstSavings=0,useDaylight=false,transitions=19,lastRule=null],firstDayOfWeek=1,minimalDaysInFirstWeek=1,ERA=1,YEAR=2015,MONTH=5,WEEK_OF_YEAR=25,WEEK_OF_MONTH=3,DAY_OF_MONTH=16,DAY_OF_YEAR=167,DAY_OF_WEEK=3,DAY_OF_WEEK_IN_MONTH=3,AM_PM=1,HOUR=5,HOUR_OF_DAY=17,MINUTE=28,SECOND=46,MILLISECOND=808,ZONE_OFFSET=28800000,DST_OFFSET=0] cal2:java.util.GregorianCalendar[time=1434446926837,areFieldsSet=true,areAllFieldsSet=true,lenient=true,zone=sun.util.calendar.ZoneInfo[id="Asia/Shanghai",offset=28800000,dstSavings=0,useDaylight=false,transitions=19,lastRule=null],firstDayOfWeek=1,minimalDaysInFirstWeek=1,ERA=1,YEAR=2015,MONTH=5,WEEK_OF_YEAR=25,WEEK_OF_MONTH=3,DAY_OF_MONTH=16,DAY_OF_YEAR=167,DAY_OF_WEEK=3,DAY_OF_WEEK_IN_MONTH=3,AM_PM=1,HOUR=5,HOUR_OF_DAY=17,MINUTE=28,SECOND=46,MILLISECOND=837,ZONE_OFFSET=28800000,DST_OFFSET=0] date:Tue Jun 16 17:28:46 CST 2015
2.4 完整代码
TestCase类的testCreateBeanObject方法完整代码如下所示:
package com.souvc.test;import java.util.Calendar;import java.util.Date;import org.junit.Test;import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;public class TestCase { /** 测试实例化Spring容器示例 */ @Test public void testInitContext() { String conf = "applicationContext.xml"; ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(conf); System.out.println(ac); } /** 测试Spring支持的多种JavaBean对象创建方式 */ @Test public void testCreateBeanObject() { // 实例化Spring容器示例 String conf = "applicationContext.xml"; ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(conf); // 1. 用构造器来实例化的方式。 // 利用Spring调用构造器 GregorianCalendar 创建 Calendar实例. // Calendar cal1 = (Calendar)ac.getBean("calendarObj1"); //方式1 Calendar cal1 = ac.getBean("calendarObj1", Calendar.class); // 方式2 System.out.println("cal1:" + cal1); // 2. 使用静态工厂方法实例化的方式。 // 利用Spring调用 Calendar 的静态工厂方法getInstance() 创建 Calendar实例. Calendar cal2 = ac.getBean("calendarObj2", Calendar.class); System.out.println("cal2:" + cal2); // 3. 使用实例工厂方法实例化的方式。 // 利用Spring创建 GregorianCalendar 对象作为工厂, 调用getTime()方法创建Date类型对象实例. Date date = ac.getBean("dateObj", Date.class); System.out.println("date:" + date); }}
applicationContext.xml 源码:
3 如何控制Bean实例化
3.1 问题
测试Bean的作用域、Bean的生命周期回调、Bean对象的创建时机以及如何指定bean依赖关系。
3.2 步骤
步骤一:Bean对象的创建模式
1. 新建包com.souvc.dao , 新建类 ExampleBean。
package com.souvc.dao;public class ExampleBean { public ExampleBean() { System.out.println("实例化ExampleBean"); } public void execute() { System.out.println("执行ExampleBean处理"); }}
2. 在applicationContext.xml文件中,配置ExampleBean,代码如下所示:
3. 在TestCase中新建测试方法testExampleBean(),在方法中从Spring中获取两个ExampleBean类型对象,通过比较操作 符“ == ” 进行比较,如果输出结果为true,则表明两次获取的是同一个对象,即创建对象的方式单例模式,代码如下所示:
@Test public void testExampleBean() { // 实例化Spring容器示例 String conf = "applicationContext.xml"; ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(conf); // 获取ExampleBean对象 ExampleBean bean1 = ac.getBean("exampleBean", ExampleBean.class); ExampleBean bean2 = ac.getBean("exampleBean", ExampleBean.class); System.out.println(bean1 == bean2); // 关闭Spring容器, 注意AbstractApplicationContext类型定义了 close()方法 //AbstractApplicationContext ctx = (AbstractApplicationContext) ac; //ctx.close(); }
4. 运行testExampleBean()方法,控制台输出结果如下:
- 实例化ExampleBean
- true
上述运行结果可以看得出在软件运行期间ExampleBean的构造器只被调用过一次, 创建过一个对象,两次获得引用变量bean1, bean2,通过比较操作符“ ==” 进行比较的输出结果为true, 说明是引用了同一个对象, 也就说明Spring容器创建Bean对象是唯一实例, 是单例对象。
5. 修改applicationContext.xml,设置创建Bean的模式为原型模式(prototype)
6. 再次运行testExampleBean()方法,控制台输出结果如下:
- 实例化ExampleBean
- 实例化ExampleBean
- false
这个结果说明调用了2次ExampleBean类的构造方法创建了两个Bean对象,比较结果是false表示bean1和bean2引用了这两个不同的对象, 这样创建bean就不再是单例模式了。
步骤二:Bean对象的初始化和销毁
1. 修改ExampleBean类,加入方法init和方法destroy,代码如下所示:
package com.souvc.dao;public class ExampleBean { public ExampleBean() { System.out.println("实例化ExampleBean"); } public void execute() { System.out.println("执行ExampleBean处理"); } public void init() { System.out.println("初始化ExampleBean对象"); } public void destroy() { System.out.println("销毁ExampleBean对象"); }}
2. 修改applicationContext.xml,希望在bean对象创建后自动调用init()方法,代码如图-12所示:
3.运行testExampleBean()方法,自定义的初始化的方法在对象被创建后调用,如图-13所示:
实例化ExampleBean初始化ExampleBean对象实例化ExampleBean初始化ExampleBean对象false
4.修改applicationContext.xml,希望在bean对象销毁前自动调用destroy方法,bean对象在spring容器关闭的时候被销毁,代码如图-14所示:
5.修改testExampleBean()方法,关闭ApplicationContext对象,代码如图-15所示:
@Test public void testExampleBean() { // 实例化Spring容器示例 String conf = "applicationContext.xml"; ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(conf); // 获取ExampleBean对象 ExampleBean bean1 = ac.getBean("exampleBean", ExampleBean.class); ExampleBean bean2 = ac.getBean("exampleBean", ExampleBean.class); System.out.println(bean1 == bean2); // 关闭Spring容器, 注意AbstractApplicationContext类型定义了 close()方法 AbstractApplicationContext ctx = (AbstractApplicationContext) ac; ctx.close(); }
6.运行testExampleBean()方法,控制台输出结果如图
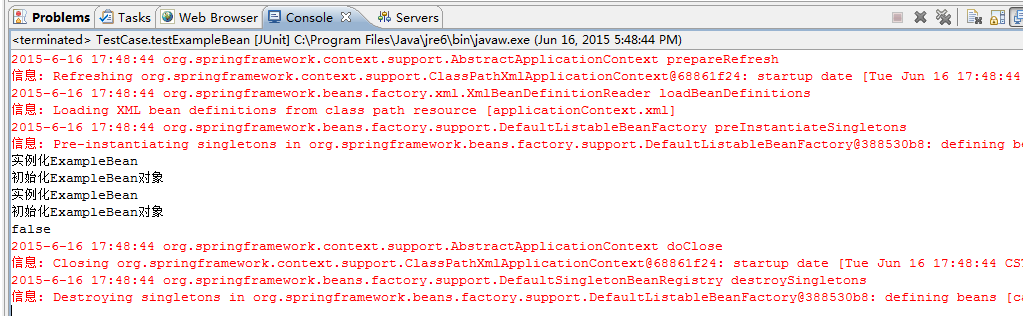
控制台没有输出预期的“销毁ExampleBean对象”的结果。原因在于applicationContext.xml文件中设置的destroy-method属性仅仅对单例模式起作用,在prototype模式下没有意义。
7.修改applicationContext.xml,使用singleton模式创建Bean对象,代码所示:
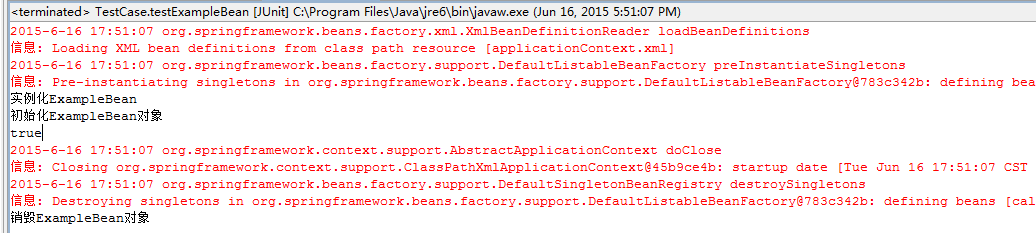
8.运行testExampleBean()方法,控制台输出了“销毁ExampleBean对象” ,代码如下图所示。
9.在顶级的<beans/>元素中的default-init-method属性以及default-destroy-method属性,可以为容器所有<bean>指定初始化回调方法以及指定销毁回调方法,代码如下图所示:
步骤三:Bean对象的创建时机
1. 注释testExampleBean中如图所示的代码。
@Test public void testExampleBean() { // 实例化Spring容器示例 String conf = "applicationContext.xml"; ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(conf); // 获取ExampleBean对象 //ExampleBean bean1 = ac.getBean("exampleBean", ExampleBean.class); //ExampleBean bean2 = ac.getBean("exampleBean", ExampleBean.class); //System.out.println(bean1 == bean2); // 关闭Spring容器, 注意AbstractApplicationContext类型定义了 close()方法 //AbstractApplicationContext ctx = (AbstractApplicationContext) ac; //ctx.close(); }
2. 运行testExampleBean方法,控制台输出结果
实例化ExampleBean
初始化ExampleBean对象控制台打印结果,说明默认情况下ExampleBean在Spring容器被创建时就会创建。
3. 修改applicationContext.xml,通过设置配置文件属性lazy-init="true",可以改变Spring容器创建对象的时机,代码如图-22所示:
4.运行testExampleBean方法,控制台没有输出信息,因为对象并没有被实例化,或者说,实例化被延迟了。
5. 去除 testExampleBean方法注释掉的代码,
@Test public void testExampleBean() { // 实例化Spring容器示例 String conf = "applicationContext.xml"; ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(conf); // 获取ExampleBean对象 ExampleBean bean1 = ac.getBean("exampleBean", ExampleBean.class); ExampleBean bean2 = ac.getBean("exampleBean", ExampleBean.class); System.out.println(bean1 == bean2); // 关闭Spring容器, 注意AbstractApplicationContext类型定义了 close()方法 AbstractApplicationContext ctx = (AbstractApplicationContext) ac; ctx.close(); }
6.运行testExampleBean方法
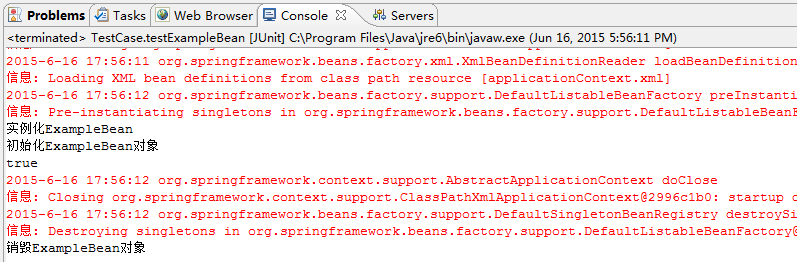
从输出结果可以看出,当使用ExampleBean对象时,才被创建,即,设置lazy-init="true"属性后,对象不使用不创建。
7.在顶级的<beans/>元素中的default-lazy-init属性,可以为容器所有<bean>指定延迟实例化特性
步骤四:指定bean依赖关系
1. 新建类ExampleBean1,代码如下所示:
package com.souvc.dao;public class ExampleBean1 { public ExampleBean1() { System.out.println("实例化ExampleBean1"); }}
2. 修改applicationContext.xml文件,将ExampleBean依赖ExampleBean1
3. 运行testExampleBean方法,控制台输出结果如图-27所示:
实例化ExampleBean1实例化ExampleBean初始化ExampleBean对象true2015-6-16 18:02:00 org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext doClose信息: Closing org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext@2996c1b0: startup date [Tue Jun 16 18:02:00 CST 2015]; root of context hierarchy2015-6-16 18:02:00 org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry destroySingletons信息: Destroying singletons in org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory@783c342b: defining beans [calendarObj1,calendarObj2,calendarObj3,dateObj,exampleBean,exampleBean1]; root of factory hierarchy销毁ExampleBean对象
可以看出,由于ExampleBean依赖于ExampleBean1,因此在创建ExampleBean的同时,也创建了ExampleBean1。
3.3 完整代码
ExampleBean类的完整代码如下所示:
package com.souvc.dao;public class ExampleBean { public ExampleBean() { System.out.println("实例化ExampleBean"); } public void execute() { System.out.println("执行ExampleBean处理"); } public void init() { System.out.println("初始化ExampleBean对象"); } public void destroy() { System.out.println("销毁ExampleBean对象"); }}
ExampleBean1 源码:
package com.souvc.dao;public class ExampleBean1 { public ExampleBean1() { System.out.println("实例化ExampleBean1"); }}
TestCase 源码:
package com.souvc.test;import java.util.Calendar;import java.util.Date;import org.junit.Test;import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;import org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext;import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;import com.souvc.dao.ExampleBean;public class TestCase { /** 测试实例化Spring容器示例 */ @Test public void testInitContext() { String conf = "applicationContext.xml"; ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(conf); System.out.println(ac); } /** 测试Spring支持的多种JavaBean对象创建方式 */ @Test public void testCreateBeanObject() { // 实例化Spring容器示例 String conf = "applicationContext.xml"; ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(conf); // 1. 用构造器来实例化的方式。 // 利用Spring调用构造器 GregorianCalendar 创建 Calendar实例. // Calendar cal1 = (Calendar)ac.getBean("calendarObj1"); //方式1 Calendar cal1 = ac.getBean("calendarObj1", Calendar.class); // 方式2 System.out.println("cal1:" + cal1); // 2. 使用静态工厂方法实例化的方式。 // 利用Spring调用 Calendar 的静态工厂方法getInstance() 创建 Calendar实例. Calendar cal2 = ac.getBean("calendarObj2", Calendar.class); System.out.println("cal2:" + cal2); // 3. 使用实例工厂方法实例化的方式。 // 利用Spring创建 GregorianCalendar 对象作为工厂, 调用getTime()方法创建Date类型对象实例. Date date = ac.getBean("dateObj", Date.class); System.out.println("date:" + date); } @Test public void testExampleBean() { // 实例化Spring容器示例 String conf = "applicationContext.xml"; ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(conf); // 获取ExampleBean对象 ExampleBean bean1 = ac.getBean("exampleBean", ExampleBean.class); ExampleBean bean2 = ac.getBean("exampleBean", ExampleBean.class); System.out.println(bean1 == bean2); // 关闭Spring容器, 注意AbstractApplicationContext类型定义了 close()方法 AbstractApplicationContext ctx = (AbstractApplicationContext) ac; ctx.close(); }}
applicationContext.xml 源码:
4 利用Spring实现bean属性setter方式注入
4.1 问题
JDBCDataSource类封装了管理数据库连接的方法getConnection(), 这个方法在执行之前需要数据库连接参数: 数据库驱动, 连接URL, 用户名和密码.
JDBCDataSource代码如下:
package com.souvc.dao;import java.io.Serializable;import java.sql.Connection;import java.sql.DriverManager;import java.sql.SQLException;public class JDBCDataSource implements Serializable { private String driver; private String url; private String user; private String pwd; public String getDriver() { return driver; } public void setDriver(String driver) { try { // 注册数据库驱动 Class.forName(driver); this.driver = driver; } catch (Exception e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } public String getUrl() { return url; } public void setUrl(String url) { this.url = url; } public String getUser() { return user; } public void setUser(String user) { this.user = user; } public String getPwd() { return pwd; } public void setPwd(String pwd) { this.pwd = pwd; } public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException { Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, pwd); return conn; } public void close(Connection conn) { if (conn != null) { try { conn.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }}
利用Spring实现JDBCDataSource对象的创建, 再使用setter注入的方式将数据库连接参数注入给JDBCDataSource。这样就可以正常的调用getConnection()方法获得数据库连接了.
4.2 方案
利用Spring配置文件applicationContext.xml配置bean, 并且setter参数注入JDBCDataSource的连接参数, 这样Spring在创建JDBCDataSource对象以后就会自动化的调用setter方法注入数据库连接参数.
applicationContext.xml配置bean参考代码如下:
4.3 步骤
步骤一:新建工程,导入jar包
新建名为SouvcSpringIoC的web工程,在该工程导入如下面所示的6个jar包, 包括Spring API 和 Oracle JDBC Driver或者mysql JDBC DRIVER。
commons-logging.jar spring-core.jar spring-context.jar spring-beans.jar spring-expression.jar ojdbc5.jar
步骤二:创建被Spring管理的JDBCDataScorce类, 用于连接到数据库
代码如下所示:
package com.souvc.dao;import java.io.Serializable;import java.sql.Connection;import java.sql.DriverManager;import java.sql.SQLException;public class JDBCDataSource implements Serializable { private String driver; private String url; private String user; private String pwd; public String getDriver() { return driver; } public void setDriver(String driver) { try { // 注册数据库驱动 Class.forName(driver); this.driver = driver; } catch (Exception e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } public String getUrl() { return url; } public void setUrl(String url) { this.url = url; } public String getUser() { return user; } public void setUser(String user) { this.user = user; } public String getPwd() { return pwd; } public void setPwd(String pwd) { this.pwd = pwd; } public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException { Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, pwd); return conn; } public void close(Connection conn) { if (conn != null) { try { conn.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }}
步骤三:新建applicationContext.xml, 并且增加setter代码注入JDBC参数
在配置文件中声明JDBCDataSource实例的bean ID为"dataSource", 该文件的核心代码如图-29所示:
步骤四:新建TestCase类,添加测试方法testJDBCDataSource()
新建的testJDBCDataSource()方法中,从Spring中获取ID为"dataSource"的 JDBCDataSource对象, Spring会在创建JDBCDataSource对象之后调用setter方法注入JDBC连接参数:
package com.souvc.test;import java.sql.Connection;import org.junit.Test;import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;import com.souvc.dao.JDBCDataSource;public class TestCase { /** Setter 注入测试 */ @Test public void testJDBCDataSource() throws Exception { String conf = "applicationContext.xml"; ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(conf); System.out.println(ac); JDBCDataSource ds = ac.getBean("dataSource", JDBCDataSource.class); Connection conn = ds.getConnection(); System.out.println(conn); }}
步骤五:运行testJDBCDataSource方法
运行testJDBCDataSource方法,控制台的输出结果:
org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext@1a9334: startup date [Wed Jun 17 09:19:41 CST 2015]; root of context hierarchycom.mysql.jdbc.ConnectionImpl@9a8a68
如果能够输出如上结果, 说明能够成功的获取Oracle JDBC 连接, 也就说明Spring成功的调用Setter方法注入了数据库连接参数。
4.4 完整代码
JDBCDataSource类的完整代码如下所示:
package com.souvc.dao;import java.io.Serializable;import java.sql.Connection;import java.sql.DriverManager;import java.sql.SQLException;public class JDBCDataSource implements Serializable { private String driver; private String url; private String user; private String pwd; public String getDriver() { return driver; } public void setDriver(String driver) { try { // 注册数据库驱动 Class.forName(driver); this.driver = driver; } catch (Exception e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } public String getUrl() { return url; } public void setUrl(String url) { this.url = url; } public String getUser() { return user; } public void setUser(String user) { this.user = user; } public String getPwd() { return pwd; } public void setPwd(String pwd) { this.pwd = pwd; } public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException { Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, pwd); return conn; } public void close(Connection conn) { if (conn != null) { try { conn.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }}
TestCase类的完整代码如下所示:
package com.souvc.test;import java.sql.Connection;import org.junit.Test;import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;import com.souvc.dao.JDBCDataSource;public class TestCase { /** Setter 注入测试 */ @Test public void testJDBCDataSource() throws Exception { String conf = "applicationContext.xml"; ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(conf); System.out.println(ac); JDBCDataSource ds = ac.getBean("dataSource", JDBCDataSource.class); Connection conn = ds.getConnection(); System.out.println(conn); }}
applicationContext.xml文件的完整代码如下所示:
5 利用构造器参数实现依赖属性的注入
5.1 问题
OracleUserDAO是经典的数据访问接口实现类, 这个类工作必须依赖Oracle数据库连接来工作, JDBCDataSource实例可以提供Oracle数据库的连接, OracleUserDAO类 采用构造器参数的方式, 依赖JDBCDataSource类, 这样的好处是创建OracleUserDAO类必须有参数JDBCDataSource对象实例. Spring支持利用构造器注入参数创建Bean对象的方式.
UserDAO接口参考如下:
package com.souvc.dao;/** * 用户数据访问对象接口 */public interface UserDAO { /** 根据唯一用户名查询系统用户, 如果没有找到用户信息返回null */ public User findByName(String name);}
User类型参考如下:
package com.souvc.entity;import java.io.Serializable; public class User implements Serializable { private int id; private String name; private String pwd; private String phone; public User() { } public User(int id, String name, String pwd, String phone) { this.id = id; this.name = name; this.pwd = pwd; this.phone = phone; } public User(String name, String pwd, String phone) { super(); this.name = name; this.pwd = pwd; this.phone = phone; } public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getPwd() { return pwd; } public void setPwd(String pwd) { this.pwd = pwd; } public String getPhone() { return phone; } public void setPhone(String phone) { this.phone = phone; } @Override public int hashCode() { return id; } @Override public boolean equals(Object obj) { if (this == obj) return true; if (obj == null) return false; if (obj instanceof User) { User o = (User) obj; return this.id == o.id; } return true; } @Override public String toString() { return id+","+name+","+pwd+","+phone; } }
OracleUserDAO类参考如下:
package com.souvc.dao;import java.sql.Connection;import java.sql.PreparedStatement;import java.sql.ResultSet;import java.sql.SQLException;public class OracleUserDAO implements UserDAO { private JDBCDataSource dataSource; /** 创建 OracleUserDAO 对象必须依赖于JDBCDataSource实例 */ public OracleUserDAO(JDBCDataSource dataSource) { this.dataSource = dataSource; } /** 根据唯一用户名查询系统用户, 如果没有找到用户信息返回null */ public User findByName(String name) { System.out.println("利用JDBC技术查找User信息"); String sql = "select id, name, pwd, phone from USERS where name=?"; Connection conn = null; try { conn = dataSource.getConnection(); PreparedStatement ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql); ps.setString(1, name); ResultSet rs = ps.executeQuery(); User user = null; while (rs.next()) { user = new User(); user.setId(rs.getInt("id")); user.setName(rs.getString("name")); user.setPwd(rs.getString("pwd")); user.setPhone(rs.getString("phone")); } rs.close(); ps.close(); return user; } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); throw new RuntimeException(e); } finally { dataSource.close(conn); } }}
sql语句:
SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS=0;-- ------------------------------ Table structure for `tb_users`-- ----------------------------DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `tb_users`;CREATE TABLE `tb_users` ( `id` int(10) NOT NULL, `name` varchar(25) default NULL, `pwd` varchar(25) default NULL, `phone` varchar(11) default NULL) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;-- ------------------------------ Records of tb_users-- ----------------------------INSERT INTO `tb_users` VALUES ('1', 'tom', '123456', '18976546545');
5.2 方案
Spring支持利用构造器注入参数实例化Bean方式。只要在Spring的配置文件中增加构造器参数constructor-arg, Spring就会自动的调用有参数的构造器创建bean对象实例, 整个过程无需程序编码只需要配置applicationContext.xml文件即可, 代码参考如下:
5.3 步骤
步骤一:新建业务实体类: User类
User类代表软件中的用户实例类型, 用户对象信息存储在Oracle数据库中.User类代码如下所示:
package com.souvc.entity;import java.io.Serializable; public class User implements Serializable { private int id; private String name; private String pwd; private String phone; public User() { } public User(int id, String name, String pwd, String phone) { this.id = id; this.name = name; this.pwd = pwd; this.phone = phone; } public User(String name, String pwd, String phone) { super(); this.name = name; this.pwd = pwd; this.phone = phone; } public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getPwd() { return pwd; } public void setPwd(String pwd) { this.pwd = pwd; } public String getPhone() { return phone; } public void setPhone(String phone) { this.phone = phone; } @Override public int hashCode() { return id; } @Override public boolean equals(Object obj) { if (this == obj) return true; if (obj == null) return false; if (obj instanceof User) { User o = (User) obj; return this.id == o.id; } return true; } @Override public String toString() { return id+","+name+","+pwd+","+phone; } }
步骤二:创建Oracle数据库初始化SQL脚本, 并且执行
创建Oracle数据库的初始化SQL脚本, 在数据库中创建Users表, 并且存入实例数据用于测试需要, 在Oracle上执行这个SQL脚本. Oracle初始化SQL脚本参考如下:
-- 创建用户表 CREATE TABLE tb_users ( ID NUMBER(7, 0) , NAME VARCHAR2(50) , PWD VARCHAR2(50), PHONE VARCHAR2(50) , PRIMARY KEY (id), -- 登录用户名唯一约束 constraint name_unique unique(name) ); -- 用户ID生成序列 CREATE SEQUENCE SEQ_USERS; -- 向数据库插入模拟数据 insert into tb_users(id, name, pwd, phone) values (SEQ_USERS.nextval, 'Tom', '123', '110'); insert into tb_users(id, name, pwd, phone) values (SEQ_USERS.nextval, 'Jerry', 'abc', '119'); insert into tb_users(id, name, pwd, phone) values (SEQ_USERS.nextval, 'Andy', '456', '112');
Mysql 脚本:
SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS=0;-- ------------------------------ Table structure for `tb_users`-- ----------------------------DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `tb_users`;CREATE TABLE `tb_users` ( `id` int(10) NOT NULL, `name` varchar(25) default NULL, `pwd` varchar(25) default NULL, `phone` varchar(11) default NULL) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;-- ------------------------------ Records of tb_users-- ----------------------------INSERT INTO `tb_users` VALUES ('1', 'tom', '123456', '18976546545');
步骤三:创建UserDAO接口, 定义用户查询功能
创建UserDAO接口, 声明用户数据查询方法findByName, 该方法从数据库中根据唯一的用户名查询用户对象, 如果没有查询到对象返回null. 参考代码如下:
package com.souvc.dao;import com.souvc.entity.User;/** * 用户数据访问对象接口 */public interface UserDAO { /** 根据唯一用户名查询系统用户, 如果没有找到用户信息返回null */ public User findByName(String name);}
步骤四:创建OracleUserDAO类,实现UserDAO接口定义的功能
创建OracleUserDAO类, 实现UserDAO接口的findByName方法, 该方法用户从数据库中根据唯一的用户名查询用户对象, 如果没有查询到对象返回null. 这个方法的实现必须依赖于JDBCDataSource属性, 需要利用JDBCDataSource获得数据库连接, 进行数据查询得到用户数据. 参考代码如下:
package com.souvc.dao;import java.sql.Connection;import java.sql.PreparedStatement;import java.sql.ResultSet;import java.sql.SQLException;import com.souvc.entity.User;public class OracleUserDAO implements UserDAO { private JDBCDataSource dataSource; /** 创建 OracleUserDAO 对象必须依赖于JDBCDataSource实例 */ public OracleUserDAO(JDBCDataSource dataSource) { this.dataSource = dataSource; } /** 根据唯一用户名查询系统用户, 如果没有找到用户信息返回null */ public User findByName(String name) { System.out.println("利用JDBC技术查找User信息"); String sql = "select id, name, pwd, phone from USERS where name=?"; Connection conn = null; try { conn = dataSource.getConnection(); PreparedStatement ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql); ps.setString(1, name); ResultSet rs = ps.executeQuery(); User user = null; while (rs.next()) { user = new User(); user.setId(rs.getInt("id")); user.setName(rs.getString("name")); user.setPwd(rs.getString("pwd")); user.setPhone(rs.getString("phone")); } rs.close(); ps.close(); return user; } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); throw new RuntimeException(e); } finally { dataSource.close(conn); } }}
package com.souvc.dao;import java.sql.Connection;import java.sql.PreparedStatement;import java.sql.ResultSet;import java.sql.SQLException;import com.souvc.entity.User;public class MysqlUserDAO { private JDBCDataSource dataSource; /** 创建 MysqlUserDAO 对象必须依赖于JDBCDataSource实例 */ public MysqlUserDAO(JDBCDataSource dataSource) { this.dataSource = dataSource; } /** 根据唯一用户名查询系统用户, 如果没有找到用户信息返回null */ public User findByName(String name) { System.out.println("利用JDBC技术查找User信息"); String sql = "select id, name, pwd, phone from USERS where name=?"; Connection conn = null; try { conn = dataSource.getConnection(); PreparedStatement ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql); ps.setString(1, name); ResultSet rs = ps.executeQuery(); User user = null; while (rs.next()) { user = new User(); user.setId(rs.getInt("id")); user.setName(rs.getString("name")); user.setPwd(rs.getString("pwd")); user.setPhone(rs.getString("phone")); } rs.close(); ps.close(); return user; } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); throw new RuntimeException(e); } finally { dataSource.close(conn); } }}
步骤五:配置Spring添加OracleUserDAO的bean定义
在applicationContext.xml文件中增加OracleUserDAO的Bean定义, 利用构造器初始化属性dataSource, Spring会自动调用OracleUserDAO有参数构造器创建OracleUserDAO实例, 其中userDAO是 bean ID.
dataSource为按构造参数注入, 这个参数是引用了id为dataSource的Bean对象.
步骤六:创建测试方法testOracleUserDAO()测试构造器注入
新建testOracleUserDAO方法,在方法中利用userDAO作为Bean ID获取OracleUserDAO对象, Spring会自动的调用OracleUserDAO的有参数构造器, 注入dataSource对象, 创建OracleUserDAO对象. 再调用findByName方法测试是否能够正确连接Oracle并查询得到用户信息.
步骤七:运行testOracleUserDAO方法
运行testOracleUserDAO方法,控制台的输出结果
从输出结果可以看出调用到了OracleUserDAO对象的findByName方法, 说明Spring正确的使用构造器注入的方式bean对象将dataSource注入OracleUserDAO对象内部, 并且有正确的执行结果。
5.4 完整代码
User类的完整代码如下所示:
package com.souvc.entity;import java.io.Serializable; public class User implements Serializable { private int id; private String name; private String pwd; private String phone; public User() { } public User(int id, String name, String pwd, String phone) { this.id = id; this.name = name; this.pwd = pwd; this.phone = phone; } public User(String name, String pwd, String phone) { super(); this.name = name; this.pwd = pwd; this.phone = phone; } public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getPwd() { return pwd; } public void setPwd(String pwd) { this.pwd = pwd; } public String getPhone() { return phone; } public void setPhone(String phone) { this.phone = phone; } @Override public int hashCode() { return id; } @Override public boolean equals(Object obj) { if (this == obj) return true; if (obj == null) return false; if (obj instanceof User) { User o = (User) obj; return this.id == o.id; } return true; } @Override public String toString() { return id+","+name+","+pwd+","+phone; } }
oracle.sql文件的完整代码如下所示:
-- 创建用户表 CREATE TABLE tb_users ( ID NUMBER(7, 0) , NAME VARCHAR2(50) , PWD VARCHAR2(50), PHONE VARCHAR2(50) , PRIMARY KEY (id), -- 登录用户名唯一约束 constraint name_unique unique(name) ); -- 用户ID生成序列 CREATE SEQUENCE SEQ_USERS; -- 向数据库插入模拟数据 insert into tb_users(id, name, pwd, phone) values (SEQ_USERS.nextval, 'Tom', '123', '110'); insert into tb_users(id, name, pwd, phone) values (SEQ_USERS.nextval, 'Jerry', 'abc', '119'); insert into tb_users(id, name, pwd, phone) values (SEQ_USERS.nextval, 'Andy', '456', '112');
SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS=0;-- ------------------------------ Table structure for `tb_users`-- ----------------------------DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `tb_users`;CREATE TABLE `tb_users` ( `id` int(10) NOT NULL, `name` varchar(25) default NULL, `pwd` varchar(25) default NULL, `phone` varchar(11) default NULL) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;-- ------------------------------ Records of tb_users-- ----------------------------INSERT INTO `tb_users` VALUES ('1', 'tom', '123456', '18976546545');
UserDAO文件的完整代码如下所示:
package com.souvc.dao;import com.souvc.entity.User;/** * 用户数据访问对象接口 */public interface UserDAO { /** 根据唯一用户名查询系统用户, 如果没有找到用户信息返回null */ public User findByName(String name);}
OracleUserDAO文件的完整代码如下所示:
package com.souvc.dao;import java.sql.Connection;import java.sql.PreparedStatement;import java.sql.ResultSet;import java.sql.SQLException;import com.souvc.entity.User;public class OracleUserDAO implements UserDAO { private JDBCDataSource dataSource; /** 创建 OracleUserDAO 对象必须依赖于JDBCDataSource实例 */ public OracleUserDAO(JDBCDataSource dataSource) { this.dataSource = dataSource; } /** 根据唯一用户名查询系统用户, 如果没有找到用户信息返回null */ public User findByName(String name) { System.out.println("利用JDBC技术查找User信息"); String sql = "select id, name, pwd, phone from tb_users where name=?"; Connection conn = null; try { conn = dataSource.getConnection(); PreparedStatement ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql); ps.setString(1, name); ResultSet rs = ps.executeQuery(); User user = null; while (rs.next()) { user = new User(); user.setId(rs.getInt("id")); user.setName(rs.getString("name")); user.setPwd(rs.getString("pwd")); user.setPhone(rs.getString("phone")); } rs.close(); ps.close(); return user; } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); throw new RuntimeException(e); } finally { dataSource.close(conn); } }}
package com.souvc.dao;import java.sql.Connection;import java.sql.PreparedStatement;import java.sql.ResultSet;import java.sql.SQLException;import com.souvc.entity.User;public class MysqlUserDAO { private JDBCDataSource dataSource; /** 创建 MysqlUserDAO 对象必须依赖于JDBCDataSource实例 */ public MysqlUserDAO(JDBCDataSource dataSource) { this.dataSource = dataSource; } /** 根据唯一用户名查询系统用户, 如果没有找到用户信息返回null */ public User findByName(String name) { System.out.println("利用JDBC技术查找User信息"); String sql = "select id, name, pwd, phone from tb_users where name=?"; Connection conn = null; try { conn = dataSource.getConnection(); PreparedStatement ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql); ps.setString(1, name); ResultSet rs = ps.executeQuery(); User user = null; while (rs.next()) { user = new User(); user.setId(rs.getInt("id")); user.setName(rs.getString("name")); user.setPwd(rs.getString("pwd")); user.setPhone(rs.getString("phone")); } rs.close(); ps.close(); return user; } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); throw new RuntimeException(e); } finally { dataSource.close(conn); } }}
applicationContext.xml文件的完整代码如下所示:
TestCase文件的完整代码如下所示:
package com.souvc.test;import java.sql.Connection;import org.junit.Test;import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;import com.souvc.dao.JDBCDataSource;import com.souvc.dao.UserDAO;import com.souvc.entity.User;public class TestCase { /** Setter 注入测试 */ @Test public void testJDBCDataSource() throws Exception { String conf = "applicationContext.xml"; ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(conf); System.out.println(ac); JDBCDataSource ds = ac.getBean("dataSource", JDBCDataSource.class); Connection conn = ds.getConnection(); System.out.println(conn); } /** 构造器参数注入 */ @Test public void testMysqlUserDAO() { String conf = "applicationContext.xml"; ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(conf); // 获取MysqlUserDAO的实例 UserDAO userDAO = ac.getBean("userDAO", UserDAO.class); // 查询用户对象 User tom = userDAO.findByName("tom"); System.out.println(tom); }}
本文作者:souvc
本文出处: